In an article I wrote a while ago, I explored why Giphy.com lost a whopping 90% of its traffic. The diagnosis was clear: Google detected a significant portion of low-quality content on the website. As a result, this section was deindexed, leading to a significant drop in traffic.
Now, let’s delve into how this process works and how to protect your website. We’ll examine how low-quality content can harm:
- website indexing
- search ranking
- crawl budget
Low-Quality Content Causes Massive Problems with Deindexing
John Mueller from Google once said, “Usually when I see questions like this where it’s like, we have a bunch of articles and suddenly they’re not being indexed as much as they used to be, it’s generally less of a technical issue, and more of a quality issue.”
He further explained, “It’s more a matter of just our algorithms looking at that part of the website, or the website overall and saying, we don’t know if it actually makes that much sense for us to index so many pages here. Maybe it’s OK if we just index a smaller part of the website instead.“
From John’s statement, it’s clear that low-quality content on some pages can cause significant deindexing problems for an entire website.
Identifying the Issue
How can you determine if you’re affected? Check for the number of pages classified as “Crawled – Currently Not Indexed,”, especially around the date of core updates. If you see a spike in the number of affected pages, it might be due to sitewide quality issues.
For instance, I noticed a few significant drops around the Google Spam Update, when Google was significantly cutting down indexed pages. If you’re curious, read the article that I wrote.
Low-quality Content Causes Ranking Problems
Google has mentioned that low-quality content on some parts of a website can impact the site’s overall rankings:
Think about it like this: If you go to a restaurant and have a meal that you enjoy, you’ll likely return. But if your next few meals there are disappointing, you’ll probably stop recommending that restaurant. It’s the same with Google. Why would Google recommend a website to users if there are many low-quality pages on it?
So, if you see a ranking drop in your Google Search Console or any other ranking monitoring tool, analyze the quality of your website overall. Are there any low-quality content pages indexed in Google?
Low-Quality Content Can Drain Your Crawl Budget
According to Google’s documentation, if Google spends too much time crawling low-quality URLs, it may decide that it’s not worth the time to examine the rest of your site.
This situation could lead to many pages being classified as “Discovered Currently Not Indexed,” which, according to our statistics, is the second most common indexing problem.
What To Do? Check for Low-quality Pages
Regular monitoring of your website is crucial to ensure there are no indexed low-quality pages.
How to do this?
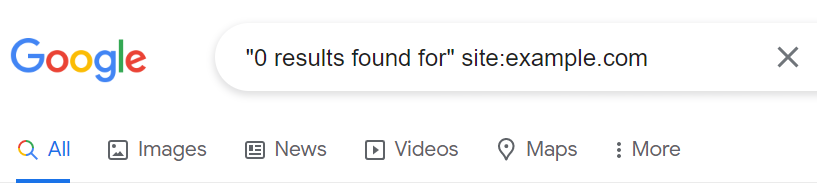
For example, you might want to verify that empty search results from your internal search engine aren’t indexed. If your website displays a “0 result found” message, you’ll want to make sure Google hasn’t indexed it.
How do you do this? It’s straightforward. Just type the following into Google’s search bar: “0 results found for” site:example.com.
Follow the same procedure with similar patterns of low-quality URLs.
This is the first and most basic step. You can then review both crawl stats in Google Search Console and in the server logs to see if Google is not wasting its crawl budget on low-quality pages.
By staying proactive in monitoring and eliminating low-quality content, you can ensure that your website maintains good standing with Google; this is essential for your site’s visibility and ranking.
Wrapping Up
In conclusion, maintaining high-quality content is crucial for your website’s health, affecting everything from indexing and rankings to your crawl budget. Keep an eye on your content quality to ensure your site stays in good standing with Google.
Anytime you have a ranking or indexing drop, think if it can be related to low-quality content on some parts of your website.